政府新闻
上海将扩展航天产业链 2023-11-22
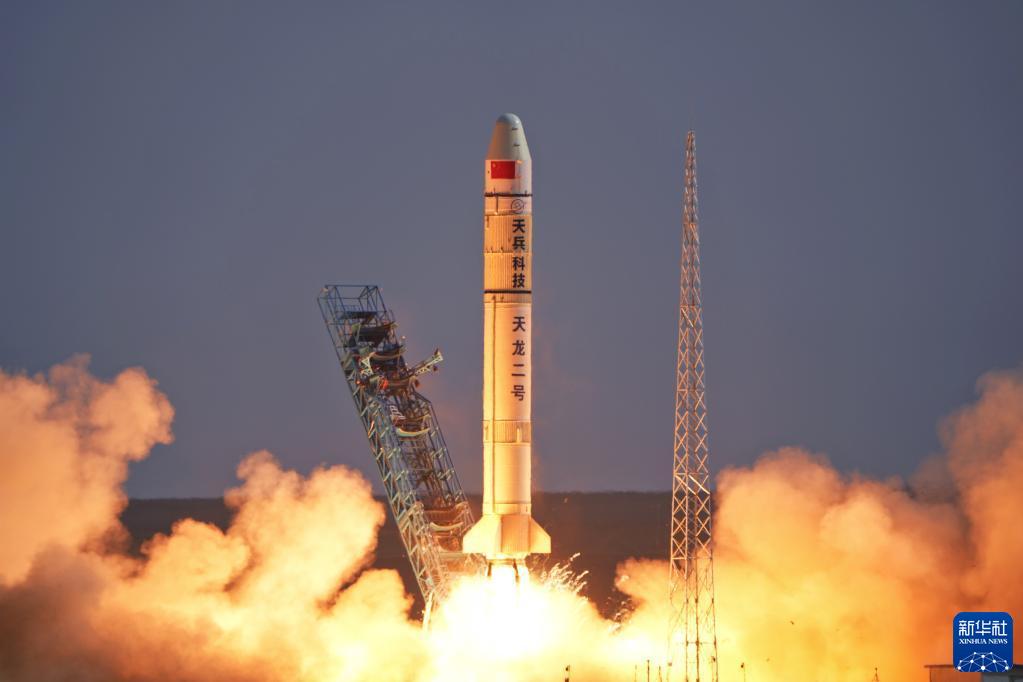

A TL 2 Y1 rocket, carrying a satellite which will be used in remote sensing imaging experiments and other technical verifications, blasts off from the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center in Northwest China on April 2, 2023.
City releases plan to boost annual production of commercial rockets
Shanghai is aiming to foster a complete industrial chain for commercial rocket production, with an annual production capacity of 50 commercial rockets and 600 commercial satellites by 2025, according to an official plan released on Monday.
The plan says Shanghai will focus on satellite manufacturing, launching, ground system equipment, spatial information applications and services, to strengthen the integrated development of satellite communications, navigation and remote-sensing technologies.
Centering on the development of three major products — new-generation medium and large carrier rockets, low-cost and highly integrated satellites, and intelligent application terminals — the city will strive to build a full-coverage industrial chain, ranging from rockets and satellites, to ground stations and terminals.
Wu Qing, vice-mayor of Shanghai, noted in April that the city has built a relatively complete spatial information industrial system, with districts having formed integrated and innovative development patterns in key sectors such as R&D, manufacturing and application.
In addition, the city is hoping to expand the application of space technologies and data services in sectors such as city governance, transportation, maritime, safety, energy and finance.
The Shanghai government will roll out supportive policies to attract and foster talent and leading firms, as well as innovative platforms such as laboratories, institutions and research centers.
By 2025, Shanghai expects its spatial information industry to exceed 200 billion yuan ($28 billion), according to the plan.
Last year, China's space industry saw remarkable achievements, including conducting a record 64 rocket launches, and completion of the Tiangong space station, one of the world's largest and most sophisticated orbiting infrastructures.
China's space industry has increasingly allowed commercial participation since 2015, following the issuance of the Medium and Long Term Development Plan for China's Civil Space Infrastructure (2015-25), which aims to push forward the healthy and rapid development of China's civilian space infrastructure.
Last July, China's first space launch site dedicated to commercial missions started construction in Wenchang, Hainan province.
This year, China's commercial space industry has witnessed a rising pace of development, with more private firms in the satellite and rocket sectors achieving successful launches.
In January, rocket startup Galactic Energy launched five satellites into orbit. In April, the Tianlong-2 Y1 carrier rocket had its maiden flight from Jiuquan, becoming China's first orbital liquid-fueled carrier rocket. Then in July, the Zhuque-2 Y2, a methane-liquid oxygen space rocket, independently developed by Beijing-headquartered LandSpace, blasted off from the Jiuquan launch site. In the same month, Galaxy Space launched China's first flat-panel communication satellite with a flexible solar array.
Last year, Shanghai released guidelines on promoting the development of the spatial information industry. Earlier in September, the city unveiled a plan to speed up construction of new infrastructure, including the establishment of commercial satellite networks.
Source:China Daily